What is Aluminum Die Casting?
Aluminum die casting is a metal manufacturing process where molten aluminum is injected under high pressure into a mold to form precise shapes—similar to plastic injection molding. However, it involves more complex systems, such as cores (for internal features), cooling channels, and ejection mechanisms.
In simple terms, the process works by forcing liquid metal through a central injection port into a pre-designed cavity, where it solidifies into the desired part. It’s a high-efficiency method for producing strong, lightweight metal components.This article explores the fundamentals of aluminum die casting, including material selection, key technologies, and diverse applications across industries.
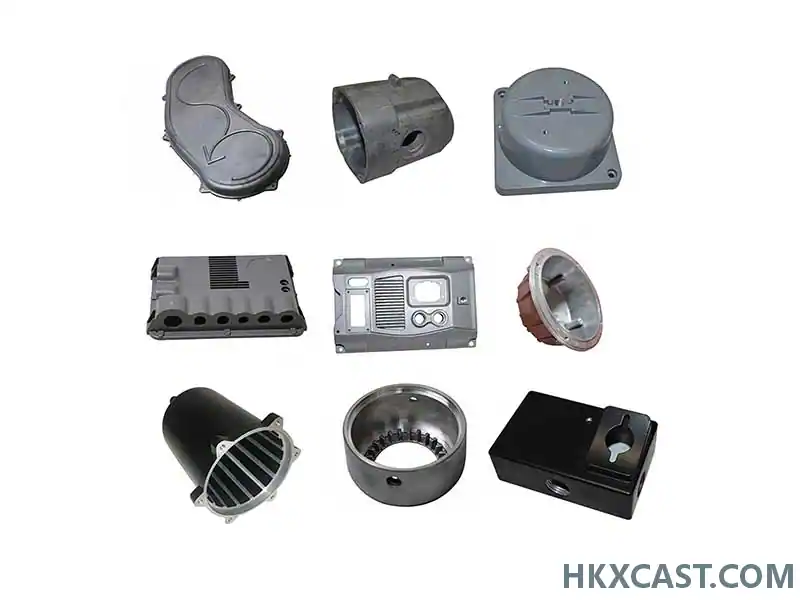

Aluminum die-castings
1. Aluminum Die Casting Alloys and Material Composition
The performance of die-cast aluminum products heavily depends on the alloy composition. Common aluminum die casting alloys like ADC12 and A380 are formulated with elements such as silicon, copper, and magnesium. These elements enhance properties like fluidity during casting, mechanical strength, and corrosion resistance. For instance, higher silicon content improves casting performance, while magnesium boosts structural integrity.
Aluminum die-casting alloys can be divided into four main types based on their composition:
- Al-Si Alloys (Aluminum-Silicon)
- These alloys typically contain:
- 8.0–11.5% silicon (Si)
- 0.3–0.8% manganese (Mn)
- 0.08–0.4% magnesium (Mg)
- Small amounts of iron (Fe, ≤0.4%), copper (Cu, ≤0.1%), zinc (Zn, ≤0.1%), titanium (Ti, ≤0.15%), and molybdenum (Mo, 0.05–0.5%)
- To improve durability, they may also include:
- Zirconium (Zr, 0.05–0.3%)
- Strontium (Sr, 30–300 ppm) or sodium/calcium (Na/Ca, 5–30 ppm)
- Phosphorus-based refiners (1–250 ppm as gallium/indium phosphide)
- These alloys typically contain:
- Al-Mg Alloys (Aluminum-Magnesium)
- Used for high strength and corrosion resistance.
- Example: AlSi10MnMg (common in car body parts).
- Features:
- Low iron (Fe), higher manganese (Mn) to prevent mold sticking.
- Adjusting magnesium (Mg) content and heat treatment can change strength and toughness.
- Al-Cu Alloys (Aluminum-Copper)
- Known for high strength and good electrical conductivity.
- Often used in structural and electrical applications.
- Al-Re Alloys (Aluminum-Rare Earth)
- Offer high heat resistance and strength at high temperatures.
- Used in demanding environments requiring corrosion resistance.
These alloys are chosen based on required properties like strength, corrosion resistance, heat resistance, and castability.
Selecting the right aluminum die cast material is critical. Factors like part complexity, intended use (e.g., structural components or heat-resistant cookware), and post-processing requirements influence the choice of die cast aluminum alloys.
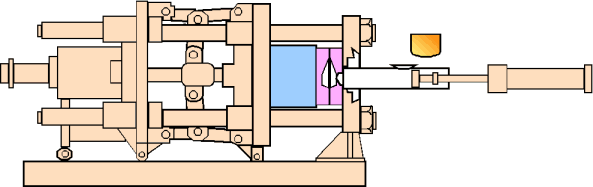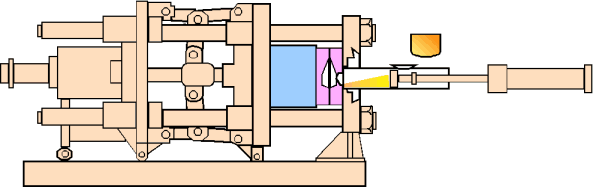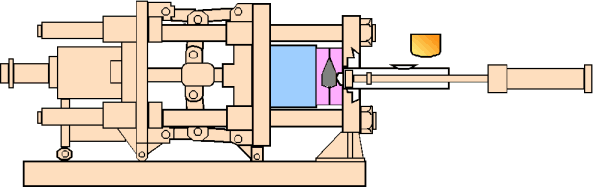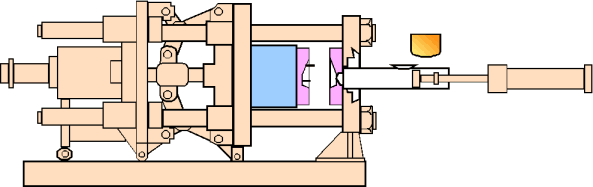
2. The Aluminum Die Casting Process Explained
The aluminum die casting process involves injecting molten alloy into a steel mold under high pressure. This method, known as high-pressure aluminum die casting, ensures precise filling of intricate molds, resulting in components with tight tolerances and smooth surfaces.
Aluminum Die Casting Production Process
- Mold Closing: The mold closes and waits for injection.
- Pouring: The robotic arm or operator ladles molten metal from the furnace into the shot sleeve.
- Injection: The metal is injected under preset process parameters.
- Mold Opening: The mold opens, with side cores retracting via angled guide pins (synchronized core pulling).
- Core Retraction: Side cores withdraw to allow ejection. For front (fixed mold) cores, retraction must occur before opening.
- Ejection: The casting is pushed out by ejector pins for removal.
- Part Removal: The casting is manually or automatically extracted. If ejector pins are locked, avoid forceful prying to prevent damage.
- Spraying: The mold cavity is cleaned, and release agent is evenly applied to both mold halves.
- Pre-Reset Mechanism: If ejector pins are beneath side cores, pull rods or pre-reset systems are used to protect the mold.
- Cycle Repeat: The mold closes again, and the process repeats.
Key equipment includes aluminum die casting machines, which control injection speed and pressure, and durable aluminum casting dies designed to withstand repeated thermal cycles. Advanced cooling systems within the molds further optimize production efficiency. Post-casting treatments, such as anodizing or powder coating, may enhance durability or aesthetics.
3. Applications of Die Cast Aluminum Products
Aluminum die casting products are integral to numerous industries due to their lightweight nature and versatility:
- Automotive: Engine housings, transmission parts, and structural components reduce vehicle weight and improve fuel efficiency.
- Electronics: Heat sinks, connectors, and device housings benefit from aluminum’s thermal conductivity and EMI shielding properties.
- Consumer Goods: Die cast aluminum cookware (pans, pots) is popular for its even heat distribution. Ensuring die cast aluminum cookware safety requires food-grade surface coatings to prevent metal leaching.
- Industrial Equipment: Yamaha’s aluminum die cast hoops for musical instruments exemplify the blend of durability and precision.
3. Choosing the Right Aluminum Die Casting Supplier
Partnering with reliable aluminum die casting manufacturers ensures quality and consistency. Key considerations include:
- Expertise in aluminum alloy die casting and material selection.
- Access to advanced aluminum die casting machines and tooling.
- Certifications for industries like automotive or food-grade applications.
Leading aluminum die casting companies (e.g., HKX Aluminum Die Casting, Aluminum Die Casting Co Inc) often provide end-to-end services, from design to finishing. For localized support, searching for “aluminum die casting near me” connects businesses with regional suppliers.
4.Conclusion
Aluminum die casting remains a cornerstone of modern manufacturing, offering cost-effective solutions for complex, high-performance parts. By understanding the nuances of aluminum die casting materials, processes, and applications, industries can leverage this technology to meet evolving demands. Whether producing automotive components, die cast aluminum pans, or industrial hardware, collaboration with experienced aluminum die casting suppliers ensures optimal results in quality and functionality.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: Is die cast aluminum cookware safe?
A: Yes, when coated with non-reactive layers (e.g., ceramic or anodized) to prevent metal contact with food. Choose certified suppliers for safety.
Q1: Why use aluminum for die casting?
A: Lightweight, corrosion-resistant, and ideal for complex parts due to alloys like ADC12/A380.
Q2: Benefits of high-pressure die casting?
A: Fast production, precise details, smooth surfaces, and minimal defects for mass production.
Q3: Die-cast vs. cast aluminum?
A: Die casting uses high pressure for thin, detailed parts; traditional casting suits simpler, heavier components.
Q4: Heat resistance of die-cast parts?
A: Yes, alloys with silicon/magnesium handle high temps, used in engines and machinery.
Q5: How to maintain aluminum cookware?
A: Avoid abrasives, hand wash gently, and replace if coatings wear off.
Q6: Key industries using die-cast aluminum?
A: Automotive, electronics, consumer goods, and industrial equipment.
Q7: How to pick a supplier?
A: Check certifications, industry experience, and advanced equipment (e.g., high-pressure machines).
Q8: Are die-cast products recyclable?
A: Yes, aluminum is 100% recyclable, supporting eco-friendly manufacturing.


